Setup swarm
This tutorial might help you if you are deploying a stack of micro-service across a cluster of nodes using Docker Swarm mode. You can always achieve this goal using different platforms such as Kubernetes or Mesos, but it is almost always a more complicated process.
For the purpose of this tutorial we’ll deploy the following set of services in a cluster.
| Microservice | Description | Source | Docker image |
| Main | proxy service | source | rabbie/dfn-poc:main-service |
| Auth | a mock auth service | source | rabbie/dfn-poc:auth-service |
| Data | a mock data service | source | rabbie/dfn-poc:data-service |
Pre-requisites
- Working knowledge of docker and containers. If you are familiar with Docker but do not know what swarm is, I would recommend reading this documentation before proceeding.
- A cluster of Linux nodes, interconnected through a network interface. For this tutorial, I will use a cluster of virtual machines in Google Cloud running Ubuntu 20.04 LTS.
- Docker server and client pre-installed on all nodes.
- At least one node should have access to the internet (Because our docker images are hosted in the cloud. This requirement can be skipped if we have a local container registry)
Overall solution
Basically what we are about to do can be broken down into 5 steps.
- Create a docker swarm
- Define the swarm services
- Create the swarm stack
- Deploy the stack
- Monitor and engage
Easy! right?
Step 1: Create the “swarm”
Every docker swarm cluster has nodes of 2 roles.
- Manager – we communicate with the cluster through this node
- Worker – carries out tasks assigned by manager
First we will create a manager and invite workers to join the cluster.
Step 1.1 : Create the Manager
SSH into one of your nodes and type this easy one-liner. (If you only have one node exposed to the public, this node should be it)
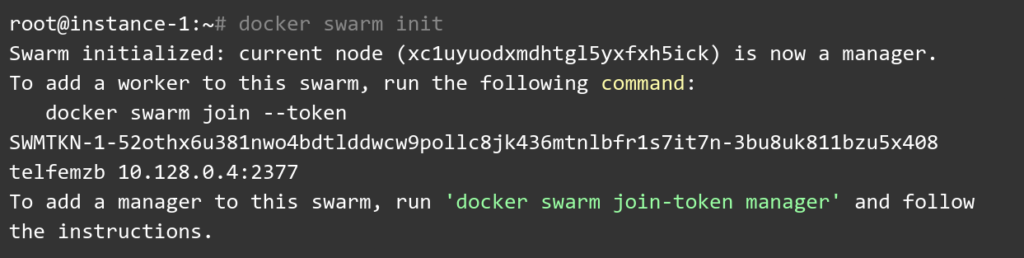
The response is self-explanatory. This very node has now become a manager and the token can be used to add nodes to this cluster. However, swarm allows having multiple managers per cluster as well.
Step 1.2 : Create a Worker
Now connect to each of the worker nodes and run the one-liner which was included in the response above.
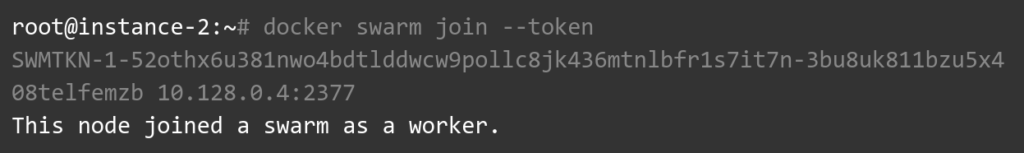
Now we have successfully created a swarm of two nodes. In the next part of this tutorial, we will look into the concepts of a microservice in the docker swarm context.